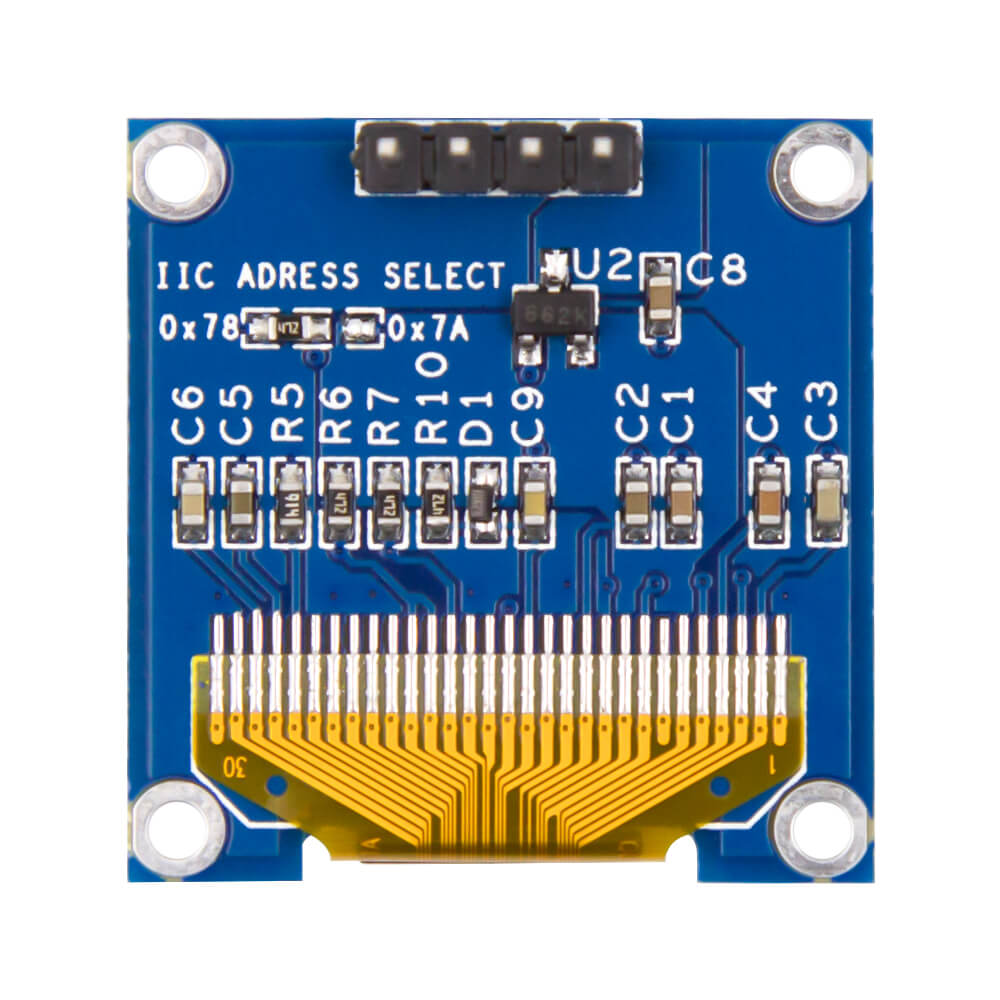
Blue I2C IIC OLED LCD Module
- $4.90
- Brand: Kuongshun Electronic
- Availability: In Stock
- SKU: AA139
0.96 Inch/1.3 Inch OLED LCD LED Display Module For Arduino IIC I2C Communicate DC 3V-5V Description: What is OLED?OLED...
Tags:
0.96 Inch/1.3 Inch OLED LCD LED Display Module For Arduino IIC I2C Communicate DC 3V-5V
Description:
What is OLED?
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) is a self light-emitting technology composed of a thin, multi-layered organic film placed between an anode and cathode. In contrast to LCD technology, OLED does not require a backlight. OLED possesses high application potential for virtually all types of displays and is regarded as the ultimate technology for the next generation of flat-panel displays.
Features:
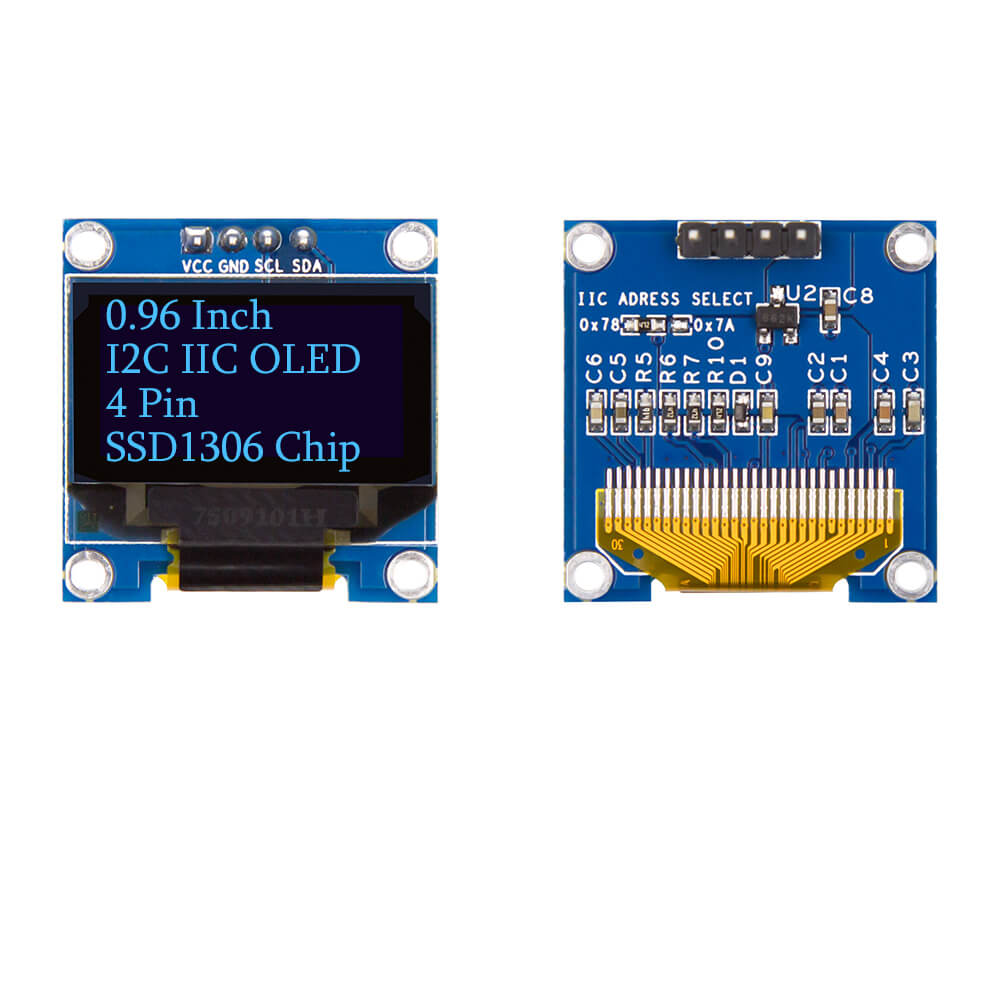
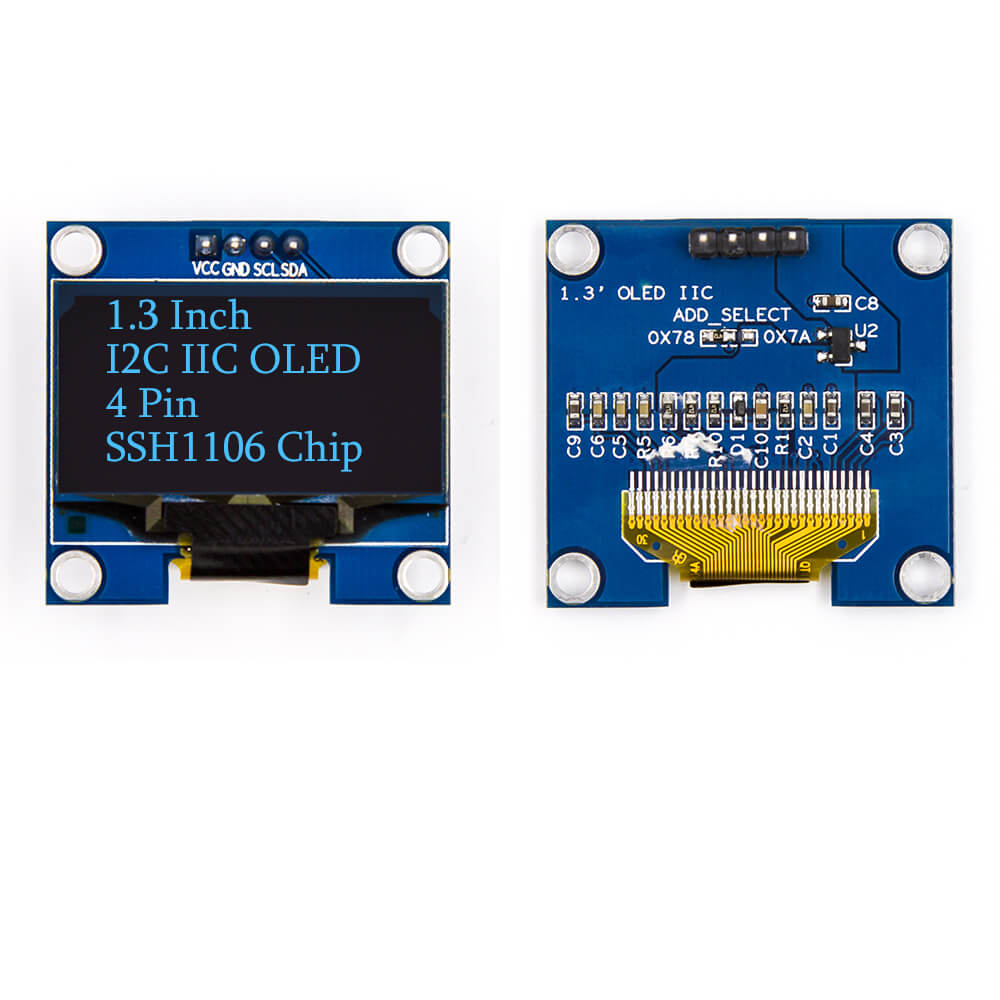
This is an OLED monochrome 128x64 dot matrix display module with I2C Interface. Comparing to LCD, OLED screens are way more competitive, which has a number of advantages such as high brightness, self-emission, high contrast ratio, wide viewing angle, wide temperature range, and low power consumption.
- Interface: I2C (3.3V logic level)
- Resolution: 128*64
- Angle of view: >160 degree
- Display dimension: 0.96 inch/1.3 inch
- Driver IC: SSD1306/SSH1106
- Power supply: 3.3V~5VDC
- Operating temperature: -20~70
- Application: smart watch, MP3, thermometer, instruments, DIY projects, etc.
The use of OLED technology offers the following advantages for flat-panel displays?
- A simplified manufacturing process compared to TFT-LCD (See comparison of Picture 1 and Picture 2 below)
- Self-emitting light, in contrast to the required backlight for TFT-LCD
- High luminosity
- Lightweight and thin (less than 2 mm)
- Low operating voltage and power consumption
- Quick response (~ ? second level)
- Wide range of operating temperatures (-40c to 85c)
How Does OLED Emit Light?
OLED"s basic structure consists of organic materials positioned between the cathode and the anode, which is composed of electric conductive transparent Indium Tin Oxide (ITO). The organic materials compose a multi-layered thin film, which includes the Hole Transporting Layer (HTL), Emission Layer (EML) and the Electron Transporting Layer (ETL). By applying the appropriate electric voltage, holes and electrons are injected into the EML from the anode and the cathode, respectively. The holes and electrons combine inside the EML to form excitons, after which electroluminescence occurs. The transfer material, emission layer material and choice of electrode are the key factors that determine the quality of OLED components.